Our planet needs us to contribute as much as we can to save it from climate change. One great way to do it is by installing solar panels in our home to provide our home appliances with natural energy. Nevertheless, more things can take advantage of solar energy.
Besides standard homes, there are solar panels for recreational vehicles, solar panels for boats, power stations, and several devices. We must be aware of the benefits that solar panels bring to the world and take the initiative to use them and encourage others to install them too everywhere they can.
Table of Contents
- Where to apply solar panels?
- How to choose solar panels for battery?
- How to choose solar panels for battery
- A Smart Decision
Where to apply solar panels?
In today’s market, it’s possible to find small solar panels to some others able to provide large amounts of power. Therefore, we can provide solar energy objects like houses or vehicles of all kinds.
1. RVs
Solar panels for RV are a good alternative for noisy generators and allow visiting many more places as do not require the existence of public grid hook-ups.
2. Power Station (Generator)
Buying a portable power station with a solar panel means a very good investment; these generators would represent a reliable source of power in case of a power emergency. Moreover, people who are more worried about the environment use these as a source of consistent clean energy.
3. Small Boat
Acquiring a solar panel for boats, it’s a great way to complement our boat’s battery system. These are able to either increase or replace other charging sources. A boat can benefit from a solar panel because it can use all the energy stored in it on its behalf. There are cases where even these panels are able to store more energy than it’s needed, possibly damaging our boat’s battery if a charge controller is not configured.
How to choose solar panels for battery?
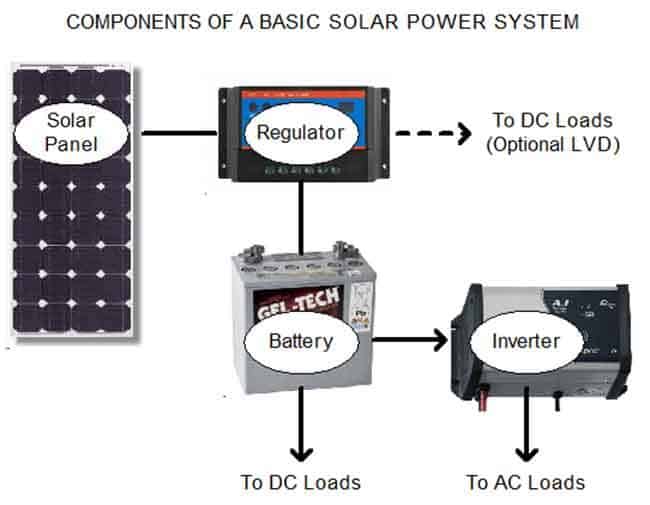
How to choose solar panels for battery
1. How many watts, amperage and volts do I need for my solar panels?
A) Watts
If we are thinking to install solar panels in our home, we must know how many kilowatts by the hour is used in our house consume. This will avoid making an excessive spend when choosing solar panels. We can easily know this measurement by looking at our power bill and searching for “Kilowatt Hours Used” or “kWh”.
To calculate the necessary amount of energy we will require, we need to multiply the hours of use by the power consumption in watts.
An average US home uses around 1 kWh, nevertheless, it can be so much more in houses where several air conditioners are used every day.
B) Amperage
The amps are the measure of the quantity of electricity our solar panel produces. The number follows a series of variables like the sun’s intensity on any given hour, the power of the solar panel, and the electric circuit component our solar panel is connected to. A 100-Watt panel is able to produce an average of 6amps.
To know the amps our panels produce, it’s possible to convert Watts into Amps by dividing the energy in Watts by the voltage.
C) Voltage
In regular conditions, a 12V solar panel is able to output around 16 and 18 volts. This is because, under unfavorable conditions, the panel needs at least 13.6 volts to charge.
To calculate volts, it’s just necessary to divide Watts by Amps.
2. Size
To determine the size of our solar power system we must know the power requirements of all things we want to provide electricity combined, and sunshine hours expected at the specific time of the year we plan to use the solar panels. With these two figured out, we divide the Watts by the hours of sunshine and the result is the approximate large of the panel we need.
There are conditions that limit some options in terms of the size of the panel we should buy. For example, there are roofs whose form does not allow to buy every possible panel. Likewise, if part of the roof where the panels will be installed is shaded most of the time, you have to maximize the remaining roof area to enhance our solar power system.
With this in mind, we will be able to determine the most accurate number of panels, their dimensions, and power generation capacity to have an efficient system at a lower cost.
3. Output Connections
An effective practice to apply to our solar panels’ system is to connect the different panels whether in a series, to increase their output voltage, to generate more direct current; or to connect them in parallel to increase the amperage of the circuit.
Wiring panels in a series is made by connecting the positive terminal of the first panel with the negative terminal of the next one until we are left with a single positive and a single negative connection.
On the other hand, to wire panels in parallel, it’s necessary to connect all the positive terminals with the next positive terminal; and negative terminals with the next negative terminal.
4. Output Power
The output power of a solar panel is expressed in units of Watts. This is possibly the most important thing to have in mind when looking at solar panels. The output power can be considered as the power production of the panel.
The direct current that a panel is able to produce certainly depends on the weather conditions. Nevertheless, standard levels of output power or wattage should not be less than 250 Watts. Multiplying the hours of sunlight the panel gets, the output power of itself is determined by the energy the panel produces in the previously mentioned Kilowatt Hours (kWh).
A Smart Decision
Solar panels systems are a little expensive in some cases but are a worthy, long-term investment. Whether it’s wanted to produce day-to-day energy to our home, vehicle, boat, or any other device, or simply to have a sunlight-charged energy backup.
Every year more and more people switch to solar power energy, and they have a point. With the increasing concerns of climate change, plus gaining independence in terms of energy supply as in the cases of recreational vehicles. Using solar panels as our source of electricity looks to be the smart decision to make these days.